‘Policy support key to adopting net metering, smart grid technologies’

Staff Correspondent
The net metering market has grown significantly in the past five years, driven by simple installation procedures, favourable government policies and the affordability of rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV), according to GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
‘Smart Grid Policy Handbook 2019’ reveals that solar PV is the most popular technology to use net metering for grid connection and small wind is at a distant second in terms of capacity connected to the grid.
Power division official said the use of solar power system under Net Metering system is becoming increasingly popular across the country. About 328 net metering systems have already been installed and at present around 7 megawatt (MW) of electricity generated from solar system is being supplied to the national grid.
Harshavardhan Reddy Nagatham, Power Analyst at GlobalData said “In countries with large solar potential and ambitious solar PV targets, rooftop solar is being looked at as a major means to achieve a significant portion of the solar or renewable power targets and net metering policies promote installations by making an installation not only reliable for backup but also profitable through the sale of surplus electricity to the grid.”
A number of countries already have net energy metering protocols and equipment in place. Countries including the US, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Australia, India and South Africa have policies that support and subsidize the installation of net meters, as well as policies that mandate utilities to provide a fair tariff to net metered customers.
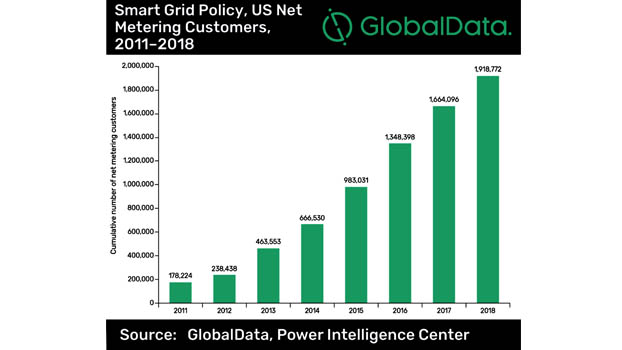
The US is among the largest markets for net meters. In the US, policy and regulatory drivers at the federal and state levels for net metering and other smart grid aspects such as demand response, energy storage and cyber-security have been the major drivers for innovation in energy efficiency programs. The number of net metering customers in the US has grown over 10 times between 2011 and 2018, increasing from around 178,000 in 2011 to over 1.9 million in 2018.
“The use of smart meters and demand response is also being actively encouraged by governments and deployed by utilities to better match the demand with the supply and reduce the peak load,”- Nagatham said.
The development of standards and interoperability protocols is something that most smart grid aspiring countries have been actively pursuing. Several countries included in the report either have smart grid standards established or have formulated roadmaps for the implementation of standardization of their respective smart grids. The US Department of Energy (DOE), along with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and other standard development organizations, has developed tools that define industry-based standards, protocols and business practices. All smart grid projects approved and funded under the various smart grid grant programs are required to address cyber-security and interoperability standards devised by the DOE.
Nagatham concludes, “The policy structure and incentives supporting smart grid development in various countries have led to significant development in smart grid projects in these markets. As a result of growing concerns over energy security, most major electricity consuming countries are in the pursuit of strengthening their grid reliability, which will help to minimize losses and use electricity efficiently.”
Net Metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid.
Under the system, the consumers, who use electricity from the grid can set up a rooftop solar home system, covering up to 70 percent capacity of the sanctioned load and can adjust their bills through an exchange arrangement by a special meter. This system will save a large amount of electricity on the subscriber’s electricity bill.
The new system is that the consumers will use their own solar power alongside the grid. But when solar power is not used during holidays or for other reasons, the consumers can sell it to the national grid.
Even on working days, they can save solar power for the grid and sell it to the power distribution company concerned. It is also called power bank.
The bill is adjusted at the end of every month on the basis of consumption of electricity and sale of solar power to the utilities. A consumer gets payment from the distribution company at bulk rate if his sale overruns the consumption.
The Power Division unveiled ‘Net Metering Guideline 2018’ on July 28 last as part of the government’s initiative to buy electricity generated at the rooftop solar home system of consumers. The government plans to generate 10 percent of electricity from renewable sources by 2020.